Software Tips
What is xRM (Extended Relationship Management)?
xRM stands for Extended Relationship Management or Any(thing) Relationship Management.
It is a strategic approach that extends the basic methods and principles of classic CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
and applies them to all business-relevant relationships. These relationships include, for example:
- Customers
- Suppliers
- Partner companies
- Employees
- Architects
- Banks and investors
- Law firms
- Associations and clubs
- Authorities
- Applicants
In the case of Any(thing) Relationship Management, the relationship management method also includes machines or devices, e.g., in the IoT context.
The aim of xRM is to manage all relevant relationships within a company in a uniform, centralized, and efficient manner—regardless of whether these relationships are between people, organizations, or things.
Examples of application scenarios for xRM
xRM systems offer flexible application possibilities that go far beyond traditional customer management and provide valuable support in a wide variety of scenarios.
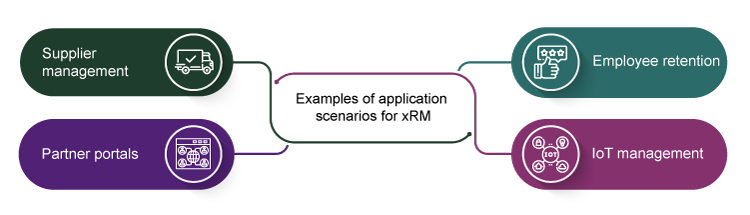
Supplier Management
Contracts, quality assurance measures, and communication in one system
Partner Portals
Structured support and management of sales partners
Employee Retention
Internal relationship management for personnel development and retention
IoT Management
Devices as "relationship objects", e.g. in remote maintenance
Advantages of Extended Relationship Management (xRM)
Extended Relationship Management (xRM) offers companies a wide range of benefits that
go beyond the capabilities of traditional Customer Relationship Management (CRM).
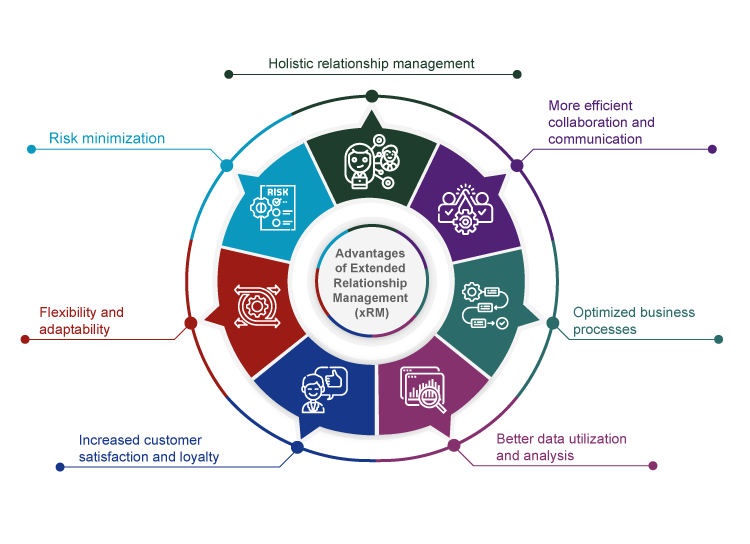
1. Holistic relationship management
xRM extends the classic CRM approach to include all relevant stakeholders—including suppliers, partners, employees, interest groups, and even physical objects (e.g., machines and real estate). This enables centralized management of complex networks of relationships with multiple hierarchical levels and roles. The result is a holistic view of all business relationships, enabling better coordination and collaboration.
2. More efficient collaboration and communication
xRM promotes internal and external communication and collaboration by providing a central platform for information exchange and interaction. This improves efficiency and reduces manual effort.
3. Optimized business processes
xRM enables the automation of business processes and the integration of different systems, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs. By mapping all of the company's processes and all stakeholders, process gaps can be closed.
4. Better data utilization and analysis
xRM offers comprehensive analysis functions that enable companies to gain valuable insights into their relationships and business processes. This supports data-driven decisions and enables better planning and control.
5. Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty
Through personalized support and the provision of relevant information and services, companies can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty. The 360-degree view of the customer allows cross-selling and upselling opportunities to be identified more quickly.
6. Flexibility and adaptability
xRM systems are generally flexible and adaptable, allowing them to be tailored to the specific requirements of a company. The systems can be seamlessly integrated into existing third-party solutions.
7. Risk minimization
By integrating diverse relationships, companies can effectively manage their communications and interactions, contributing to improved strategic positioning and risk minimization.
 Sage 100: Get started with flexible ERP software.
The ERP software for companies with individual requirements - with optional cloud services.
Sage 100: Get started with flexible ERP software.
The ERP software for companies with individual requirements - with optional cloud services. CAS genesisWorld, the leading xRM and CRM for SMEs, supports you in planning and communication. Define the individual communication stages, select the appropriate recipients using convenient filter functions, determine follow-up actions and execute multi-stage campaigns in a targeted manner via the various communication channels. You always have the success and costs of your marketing activities under control.
CAS genesisWorld, the leading xRM and CRM for SMEs, supports you in planning and communication. Define the individual communication stages, select the appropriate recipients using convenient filter functions, determine follow-up actions and execute multi-stage campaigns in a targeted manner via the various communication channels. You always have the success and costs of your marketing activities under control. With its extended functionality for any type of business relationship, Logistik-xRM is ideal for customer and partner management as well as the structured management of suppliers and subcontractors. The xRM software plans and tracks complex tasks, designs accurate marketing campaigns and brings transparency to sales activities with reliable key figures. Logistics xRM can be connected to almost any TMS.
With its extended functionality for any type of business relationship, Logistik-xRM is ideal for customer and partner management as well as the structured management of suppliers and subcontractors. The xRM software plans and tracks complex tasks, designs accurate marketing campaigns and brings transparency to sales activities with reliable key figures. Logistics xRM can be connected to almost any TMS. Sunrise CRM provides perfect support for all sales tasks, marketing, service and support as well as project planning and time recording. It is ideal for mobile field service. It is GDPR-compliant and protects your customers' data. The CRM system has a modular design and can be perfectly tailored to your company's requirements.
Sunrise CRM provides perfect support for all sales tasks, marketing, service and support as well as project planning and time recording. It is ideal for mobile field service. It is GDPR-compliant and protects your customers' data. The CRM system has a modular design and can be perfectly tailored to your company's requirements.
